|
The Ring of Fire is a horseshoe
shape situated along the Pacific Ocean from New Zealand, along the eastern edge of Asia, north across the Aleutian
Islands of Alaska, and south along the coast of North and South America. The reason why the Ring of Fire is well known is because there are frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions
that are situated within and along the Pacific Ocean.
It has been said that approximately 90% of the world's earthquakes and "two-thirds of the world's active volcanoes"
(Teachers Guide to Stratovolcanoes of the World, 2004) occur along the 40,000 km Ring of Fire.
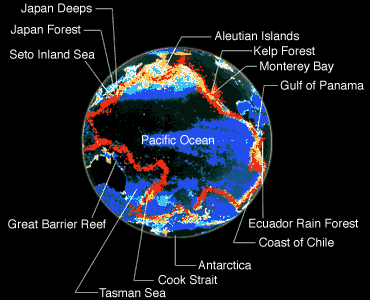
|
| http://www.kaiyukan.com/eng/profile/e-gaia.gif |
Figure 3 Global perspective of The Ring of Fire.
Source: http://www.kaiyukan.com/eng/profile/e-gaia.gif
Psychology, Ring
of Fire
And
Mount. Fuji
When
an individual experiences a trauma where it was unexpected and they were unprepared for it, a condition may arise for that
individual called Post Traumatic Stress Disorder. This disorder occurs in individuals
who go through very traumatic events such as riots, war, the loss of a loved one and natural disasters. The disorder is most commonly seen in soldiers in times of war where they experience many symptoms such
as night terrors, panic attacks, emotional numbness, and loss of memory. Generally,
symptoms become noticeable at approximately 6 months after the trauma has occurred and can remain for a life time. PTSD is a disorder that not only affects the one who has been exposed to the traumatic event, but to the
individuals that surround them such as family and friends.
Post
Traumatic Stress Disorder is described as an alteration to an individual’s brain which changes the way the brain is
structured and the way it functions. The individual with PTSD is in constant
fear of the re occurrence of the event and can re-live the event as if they were there again.
For an individual who has PTSD any reminder of the event such as a smell, noise, sound, or taste can trigger an event
for a person where there begin to have panic attacks and this can be a danger to themselves.
Some symptoms for individuals become life altering where cases have been known where night terrors have become so dangerous
in terms of the individual becoming violent not knowing what is going on and resulting in hurting themselves as well as their
loved one. They truly believe that they are back in time at the event and they
re-live the event as if it were occurring right then.
The
emotional trauma that the individual faces is extremely hard and painful to overcome the feelings and to live life again. There are a number of ways that individuals can be helped to move past the traumatic
event such as cognitive behavioural therapy. Some studies that have been conducted
have shown improvement with individuals with relaxation techniques as well as in some cases hypnosis (Jaffe, J., Segal, J., & Lisa Flores Dumke, L. F. 2007).
 |
 |
|
Symptoms of Emotional Trauma |
|
Symptom |
Characteristics |
|
Physical |
- Eating disturbances (more or less than usual)
- Sleep disturbances (more or less than usual)
- Sexual dysfunction
- Low energy
- Chronic, unexplained pain
|
|
Emotional |
- Depression, spontaneous crying, despair and hopelessness
- Anxiety
- Panic attacks
- Fearfulness
- Compulsive and obsessive behaviours
- Feeling out of control
- Irritability, angry and resentment
- Emotional numbness
- Withdrawal from normal routine and relationships
|
|
Cognitive |
- Memory lapses, especially about the trauma
- Difficulty making decisions
- Decreased ability to concentrate
- Feeling distracted
|
|
Additional Symptoms Associated with a Severe Precipitating Event
|
Symptom |
Characteristics |
|
Re-experiencing the trauma |
- intrusive thoughts
- flashbacks or nightmares
- sudden floods of emotions or images related to the traumatic event
|
|
Emotional numbing and avoidance |
- amnesia
- avoidance of situations that resemble the initial event
- detachment
- depression
- guilt feelings
- grief reactions
- an altered sense of time
|
|
Increased
arousal |
- hyper-vigilance, jumpiness, an extreme sense of being "on guard"
- overreactions, including sudden unprovoked anger
- general anxiety
- insomnia
- obsessions with death
|
(Jaffe, J., Segal, J., & Lisa Flores
Dumke, L. F. 2007).
|
|
 |
 |
|
